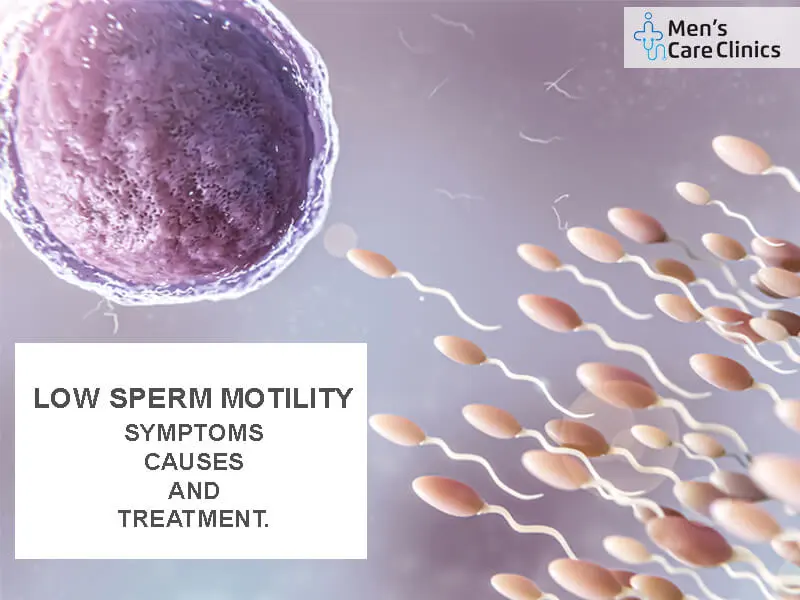
Sperm motility refers to the sperm’s ability to swim and move forward in a coordinated manner. It is an essential factor for successful fertilization because it allows sperm to reach the egg for fertilization.
Asthenozoospermia-Low Sperm Motility
Low sperm motility, also known as “Asthenozoospermia”, is a condition characterized by a decrease in the ability of sperm to move in forward direction effectively.
When sperm motility is low, it is more difficult for them to reach and penetrate the egg, reducing the likelihood of successful fertilization.
Are Low Sperm Motility and Low Sperm Count same?
No, Low sperm motility and low sperm count is two distinct factors that can contribute to male infertility. In asthenozoospermia or Low Sperm Motility, the sperm may have difficulty swimming in a straight line or may have slow or sluggish movement, making it challenging for them to reach the egg for fertilization. Low sperm count (oligospermia) means reduces the amount of sperm that can be used to fertilize an egg and can make it much harder to get pregnant.
Most of the time, 15 million sperm per milliliter (ml) or more is thought to be a normal number of sperm. Oligospermia is diagnosed when the sperm count falls below this threshold.

Symptoms of Low Sperm Motility:
Low sperm motility, or asthenozoospermia, typically has no specific symptoms that the affected person directly experiences.
However, in some cases, underlying factors contributing to low sperm motility may present with symptoms. Here are some signs that could be caused by situations that make sperm move slowly:
- Hormonal imbalances. (including changes in libido(low sex drive) and Erectile Dysfunction).
- Testicular pain and swelling.
- Abnormalities in sexual development, cognitive impairments, or other physical anomalies.
- Swelling of testicle veins “varicocele”.
Low Sperm Motility Causes
Causes of low motility sperm can be classified into two types:
- Primary.
- Secondary.
Primary asthenozoospermia: This type of asthenozoospermia is usually caused by intrinsic factors related to the sperm itself.
- Genetic abnormalities: It may be due to genetic abnormalities affecting the structure or function of the sperm tail (flagellum), which is responsible for the sperm’s movement.
Other factors such as: - Metabolic disorders: Mitochondrial dysfunction or defects in the production of ATP (the energy source for sperm motility) can impact sperm movement.
- Abnormal Sperm development: Problems during sperm maturation in the testes can lead to low sperm motility.
Secondary asthenozoospermia: This type of asthenozoospermia occurs as a result of external factors that affect sperm motility.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- An infection in the genital area.
- Testicular overheating.
- Exposure to toxins (such as chemotherapy).
- Certain medications ( antibiotics, antifungal drugs, and Chemotherapy)
- Smoking, alcohol consumption, or drug use.
- Chronic Diseases like diabetes and kidney disease.

Diagnosis
Low sperm motility, can be diagnosed through a comprehensive evaluation that typically includes the following steps:
- Physical examination: Your healthcare provider will conduct a physical examination to check for any abnormalities in the reproductive organs.
- Semen analysis: A semen analysis is a key diagnostic test for assessing sperm quality, including motility. It involves providing a semen sample, usually through masturbation, which is then analyzed in a laboratory.
A low sperm motility percentage is typically determined if less than 40-50% of the sperm show forward progressive movement. - Additional tests: Depending on the initial findings, your healthcare provider may recommend additional tests to identify any underlying causes contributing to low sperm motility. Some of these tests are:
– Testing for genes.
– Hormone assessments.
Note that the results of analyzing sperm can be different and a single test may not give a full picture. In some cases, further testing or repeat analyses may be required to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment options for low Sperm Motility
Low sperm motility can be treated in different ways, depending on what caused it and how bad it is. Here are some potential treatment approaches:
Lifestyle modifications: Making certain lifestyle changes can improve sperm motility in some cases. Some of these things are:
- Keeping a good weight.
- Staying away from toxins.
- Stop drinking and smoking.
- Getting rid of stress (through things like exercise, meditation, or therapy).
Medications: In certain cases, medications may be prescribed to address specific causes or to improve overall sperm quality. These may include:
- Hormonal therapy.
- Antioxidant supplements.
Assisted reproductive techniques: In some cases where natural conception is challenging due to severely low sperm motility, assisted reproductive techniques(IUI, IVF, ICSI) can be considered. These techniques help overcome low sperm motility by directly manipulating the sperm and facilitating fertilization.
Surgical interventions: In some cases, doctors may suggest surgery to fix abnormalities or blockages in the body that could be stopping sperm from moving.

Prevention
There are certain lifestyle practices that can help to improve sperm health.
- Eat well-rounded meals.
- Exercise regularly
- Deal with stress.
- Quit smoking.
- Avoid alcohol drinks.
- Avoid excessive heat exposure (like using laptop computers directly on the lap).
- Regularly consult with a Sexologist.