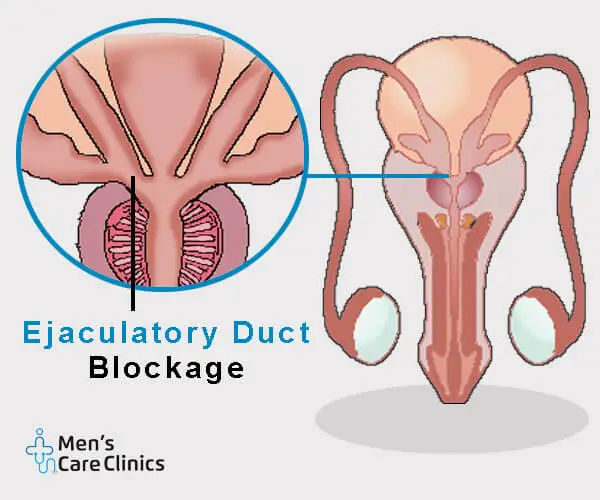
Ejaculatory Duct obstruction means that something is blocking the ducts so that sperm can’t get out of the body. There are helpful treatments available.
A blockage in the ejaculatory duct refers to an obstruction or restriction in one or both of the ejaculatory ducts. The ejaculatory ducts are thin tubes that join the seminal vesicles to the urethra. This lets sperm and seminal fluid pass through the urethra when a man ejaculates.
Types of Blockage:
Blockage can be categorized into two main types:
1 – Congenital Blockage: This type of blockage is present from birth.
- Congenital Absence: The ejaculatory ducts may occasionally be absent, resulting in a total obstruction.
- Diverticula or Cysts: This abnormal outpunching or cysts can form within the ejaculatory ducts and completely or partially restrict them.
- Stenosis: The ejaculatory ducts might narrow or constrict due to structural defects, which restrict the flow of sperm.
2– Acquired Blockage: These blockages develop later in life.
- Infection: Inflammatory disorders that induce swelling and scarring, including prostatitis or epididymitis, can block the ejaculatory ducts.
- Trauma or Surgery: The ejaculatory ducts may unintentionally be damaged or blocked during genitourinary surgery, such as prostate or bladder surgery. Seminal Vesicle.
- Calculi: Stones or calcium deposits in the seminal vesicles may move and clog the ejaculatory channels.
How common is Ejaculatory Duct Blockage?
Congenital blockages of the ejaculatory ducts are less common than acquired blockages. However, Ejaculatory duct blockage is relatively rare compared to other sexual disorders. It happens in approximately 1% – 5% of infertile men.
Signs and symptoms of Ejaculatory Duct Blockage
Signs of blockage depend on the severity of the obstruction. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain during Ejaculation.
- Pain during Sexual activity.
- Infertility.
- Low semen volume.
- Bloody in the semen.
- Feeling pain or Discomfort during urination.
Causes of Ejaculatory duct blockage:
The Ejaculatory duct can occur due to various causes. Some common causes may include:
- Cysts within the Ejaculatory duct.
- Structural abnormality of Ejaculatory ducts.
- Infection.
- Prostate or Bladder surgery.
- Calculi/Stones/Pathri.
Treatment Options:
The choice of treatment will depend on various factors, including the obstruction’s cause and severity and the blockage’s severity. Here are some potential treatment options:
- Medical Management: If the blockage is caused by an illness or inflammation, antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs may be given to treat the underlying problem.
- Transurethral Resection of Ejaculatory Ducts (TURED): Transurethral Resection of Ejaculatory Ducts (TURED): In this surgery, the ejaculatory ducts are reached by inserting a cystoscope (a thin tube with a camera) through the urethra.
- Transrectal Ultrasound-Guided Ejaculatory Duct Aspiration (TRUS-ED Aspiration): In this procedure, a thin needle is inserted through the rectum and guided by ultrasound to the site of the ejaculatory duct obstruction. The obstructing material can then be aspirated or removed.
- Balloon Dilatation: A small balloon catheter can be inserted into the ejaculatory ducts and inflated to widen the passage and break up obstructions.
- Surgical Reconstruction: In cases of more severe or complex obstructions, surgical reconstruction might be necessary. This could mean removing scar tissue, fixing broken ducts, or making a new path for the sperm.
- Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART): If an obstructed ejaculatory duct is causing infertility and can’t be fixed completely, couples may want to try ART like in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Complication of Ejaculatory Duct Blockage
Here are some potential complications associated with ejaculatory duct obstruction:
- Infertility
- Pain and Discomfort in the pelvic region.
- Hematospermia (presence of blood in semen).
- Sexual Dysfunction.
- Reduced Seminal Volume.
- Psychological Impact.